User Guide: Integration > Advanced Configurations > XPath supported operators in Volt MX Foundry
XPath in Volt MX Foundry
XPath (XML Path Language) is a query language for selecting nodes from an XML document. Volt MX Foundry supports XPath expressions to compute/filter (for example, strings, numbers, or Boolean values) a back-end response that is in XML format. Volt MX supports XPath for XML, SOAP, and JSON integration services.
For more information about XPath, refer https://www.w3schools.com/xml/xml_xpath.asp.
XPath supported operators in Volt MX Foundry
The following table details the supported operators for XPath expressions in Volt MX Foundry.
| Operators | Description |
|---|---|
| AND | Boolean and |
| OR | Boolean or |
| + | Plus |
| - | Minus |
| * | Multiply |
| Div | Division |
| Mod | Modulus (division remainder) |
| Sum | This converts the value of each node in the node-set to a number and totals the result. |
| Round | This returns the closest integer to the argument. The rounding rules follow Java conventions which are not quite the same as the XSL rules. |
-
While configuring XPath for a response, for arithmetic XPath expressions, operators and operands should be separated by at least one space ( ).
For example,
<? xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8”?>
<CATALOG>
<PLANT>
<ZONE>4</ZONE>
<PRICE>2.44</PRICE>
</PLANT>
</CATALOG>
*Sample arithmetic operations with at least one space:*
//CATALOG/PLANT/ZONE + //CATALOG/PLANT/PRICE
//CATALOG/PLANT/ZONE * //CATALOG/PLANT/PRICE
//CATALOG/PLANT/ZONE div //CATALOG/PLANT/PRICE
How to use XPath in Volt MX Foundry
- Create an integration service of an app for XML, SOAP, or JSON.
- Create an operation.
-
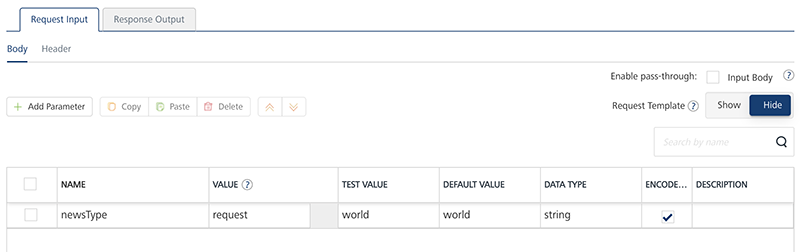
Configure the input parameters in the Request Input.
For example:
- Select the environment from the Select an Environment list.
-
Click Save and Fetch Response to view the results of the operation.
The back-end response is displayed in the XML format, in the Test Result section.
In Backend Response window, you can view the raw response as either raw data or in a tree format.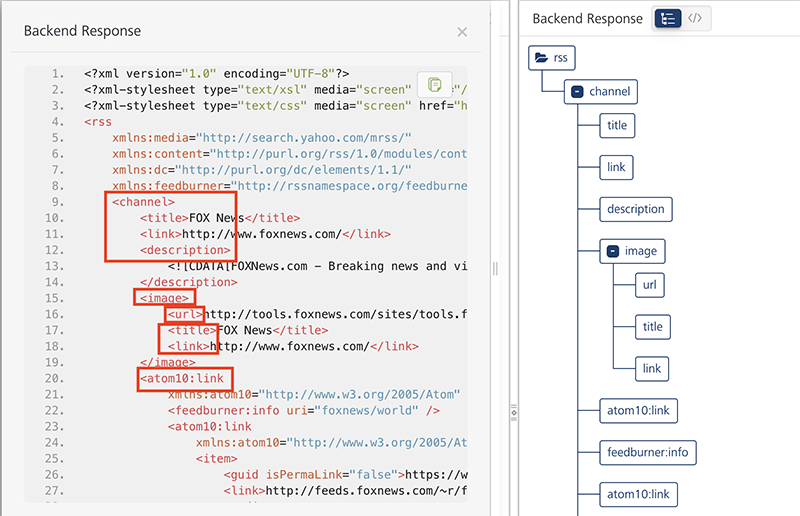
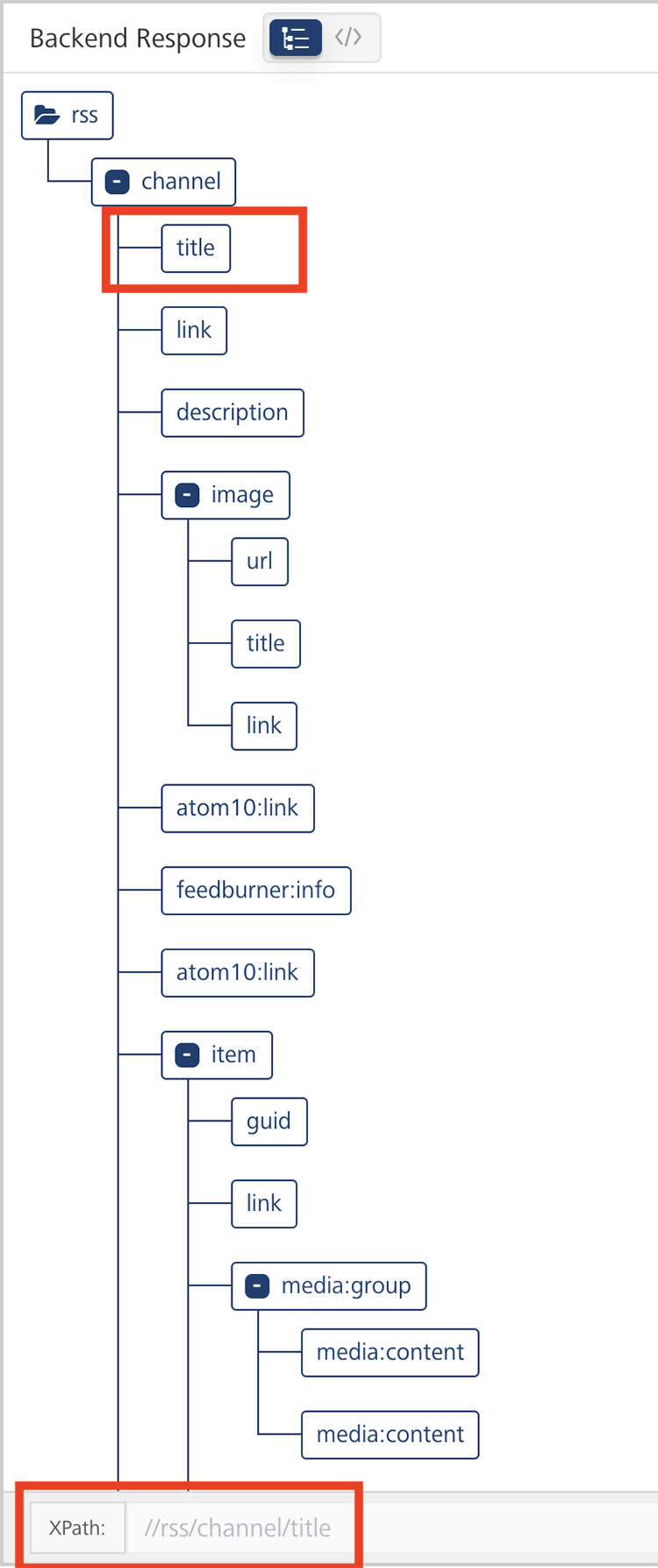
Clicking on an element in the tree to display the XPath of that tag.
-
Now apply XPath expressions for extracting the required elements from the back-end response of the service call.
For example, the following is a sample XPath expressions
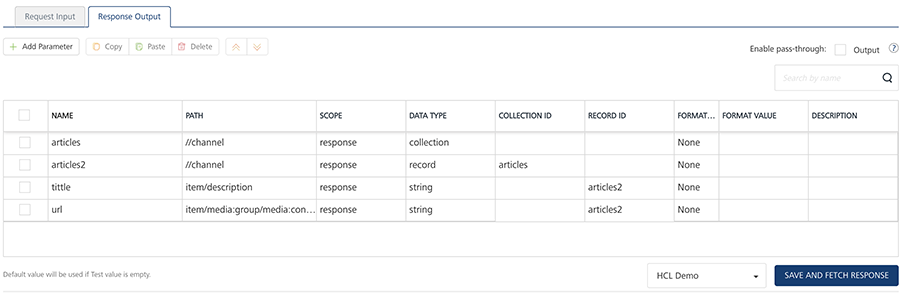
Name/ID XPath Scope Data Type Collection ID Record ID articles //channel response Collection articles2 //channel response Record articles title item/title response Sting string articles2 url item/media:group/media:content/@url response Sting string articles2 Collection - A group of data, also referred to as data set. A collection contains only records, and a record contains a string, boolean, or number values. Record - A group data elements under the specified parameter. A record can also be part of a collection. Typically, a record provides metadata to a segment. Note: For JSON integration service, the back-end response will be in JSON format. JSONPath format should contain
$in the expression.For example:
$the root object/element -
Click Save and Fetch Response again.
Now the back-end response is filtered based on the XPath expressions and displays the output in JSON format.
XPath Example Reference
The following example details a sample backend response, and XPath configurations and Output Result based on the XPath configurations
- The following is a sample Backend Response, in XML, from the Target URL of an integration service.
Sample Target URL link: http://www.mocky.io/v2/5a9fa4e92e0000630074d133
Click here to view sample Backend response
<!-- This is a Sample backend response -->
<catalog>
<book id="bk101">
<author>Gambardella, Matthew</author>
<title>XML Developer's Guide</title>
<genre>Computer</genre>
<price>44.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-10-01</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk102">
<author>Ralls, Kim</author>
<title>Midnight Rain</title>
<genre>Fantasy</genre>
<price>5.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-12-16</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk103">
<author>Corets, Eva</author>
<title>Maeve Ascendant</title>
<genre>Fantasy</genre>
<price>5.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-11-17</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk104">
<author>Corets, Eva</author>
<title>Oberon's Legacy</title>
<genre>Fantasy</genre>
<price>5.95</price>
<publish_date>2001-03-10</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk105">
<author>Corets, Eva</author>
<title>The Sundered Grail</title>
<genre>Fantasy</genre>
<price>5.95</price>
<publish_date>2001-09-10</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk106">
<author>Randall, Cynthia</author>
<title>Lover Birds</title>
<genre>Romance</genre>
<price>4.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-09-02</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk107">
<author>Thurman, Paula</author>
<title>Splish Splash</title>
<genre>Romance</genre>
<price>4.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-11-02</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk108">
<author>Knorr, Stefan</author>
<title>Creepy Crawlies</title>
<genre>Horror</genre>
<price>4.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-12-06</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk109">
<author>Kress, Peter</author>
<title>Paradox Lost</title>
<genre>Science Fiction</genre>
<price>6.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-11-02</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk110">
<author>O'Brien, Tim</author>
<title>Microsoft .NET: The Programming Bible</title>
<genre>Computer</genre>
<price>36.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-12-09</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk111">
<author>O'Brien, Tim</author>
<title>MSXML3: A Comprehensive Guide</title>
<genre>Computer</genre>
<price>36.95</price>
<publish_date>2000-12-01</publish_date>
</book>
<book id="bk112">
<author>Galos, Mike</author>
<title>Visual Studio 7: A Comprehensive Guide</title>
<genre>Computer</genre>
<price>49.95</price>
<publish_date>2001-04-16</publish_date>
</book>
</catalog>
-
The following table details the XPath for the AND operator and Output Result based on the sample response.
XPath for AND operator Output Result computerBooks: book [genre = 'Computer' and author = "O'Brien, Tim"]{ “httpStatusCode”: 200, “catalog”: [ { “computerBooks”: { “computerAuthor”: “O’Brien, Tim”, “computerTitle”: “Microsoft .NET: The Programming Bible” } }, { “computerBooks”: { “computerAuthor”: “O’Brien, Tim”, “computerTitle”: “MSXML3: A Comprehensive Guide” } } ], “opstatus”: 0 } -
The following table details the XPath for the OR operator and Output Result based on the sample response.
XPath for OR operator Output Result fictionBooks: book [genre = 'Fantasy' or genre = 'Science Fiction']{ “httpStatusCode”: 200, “catalog”: [ { “fictionBooks”: { “fictionTitle”: “Midnight Rain”, “fictionGenre”: “Fantasy” } }, { “fictionBooks”: { “fictionTitle”: “Maeve Ascendant”, “fictionGenre”: “Fantasy” } }, { “fictionBooks”: { “fictionTitle”: “Oberon’s Legacy”, “fictionGenre”: “Fantasy” } }, { “fictionBooks”: { “fictionTitle”: “The Sundered Grail”, “fictionGenre”: “Fantasy” } }, { “fictionBooks”: { “fictionTitle”: “Paradox Lost”, “fictionGenre”: “Science Fiction” } } ], “opstatus”: 0 } -
The following table details the XPaths for arithmetic operators and Output Result based on the sample response.
XPath Output Result add: count(//book[genre = 'Fantasy']) + count(//book[genre = 'Romance'])romanceCount:count(//book[genre = 'Romance'])fantasyCount:count(//book[genre = 'Fantasy'])computerAuthorCount:count(//book[genre = 'Computer' and author = "O'Brien, Tim"])fictionCount:count(//book[genre = 'Fantasy' or genre = 'Science Fiction'])subtract:count(//book[genre = 'Fantasy']) - count(//book[genre = 'Romance'])divide:count(//book[genre = 'Fantasy' or genre = 'Science Fiction']) div count(//book[genre = 'Romance'])multiply:count(//book[genre = 'Fantasy']) * count(//book[genre = 'Romance'])modulus:count(//book[genre = 'Fantasy' or genre = 'Science Fiction']) mod count(//book[genre = 'Romance']){ “add”: 6, “romanceCount”: 2, “fantasyCount”: 4, “computerAuthorCount”: 2,”fictionCount”: 5, “subtract”: 2, “divide”: 2.5, “multiply”: 8, “modulus”: “1”, “httpStatusCode”: 200 }