Button Widget for Watch
A button is a control that you use to provide input to an application or trigger an event. For example, navigating to a form, interacting with a dialog box, or confirming an action.
Click any of the following to learn about the properties found on the tabs of the Button widget.
Look Tab
On the Look tab, you define properties and behaviors related to a button widget’s appearance and position. The following sections describe each of the properties.
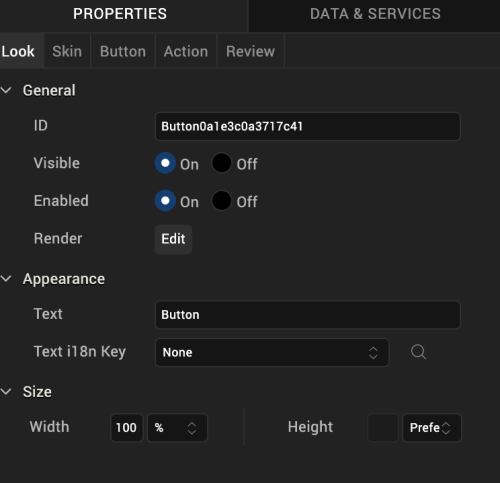
ID
Denotes the name of a widget. When a widget is added to a form, a unique name is assigned to the widget. You can rename a widget by entering a new name in the ID box.
Note: You can also rename a widget from the Project Explorer by right-clicking a widget, and then clicking Rename.
Visible
Controls whether or not the user of the app can see the widget.
- To make a widget visible, click On .
- To make a widget invisible, click Off.
Enabled
Controls whether the widget is functional or not. You can programmatically make the widget functional or nonfunctional through an action sequence, triggered by the user.
- To enable the widget, click On.
- To disable the widget, click Off.
Render
Defines whether a widget appears on a specific platform. Currently, the Watch channel supports only the Apple Watch Native and HTML5 SPA platforms. Clicking the Render property’s Edit button opens the Render Platforms dialog box.
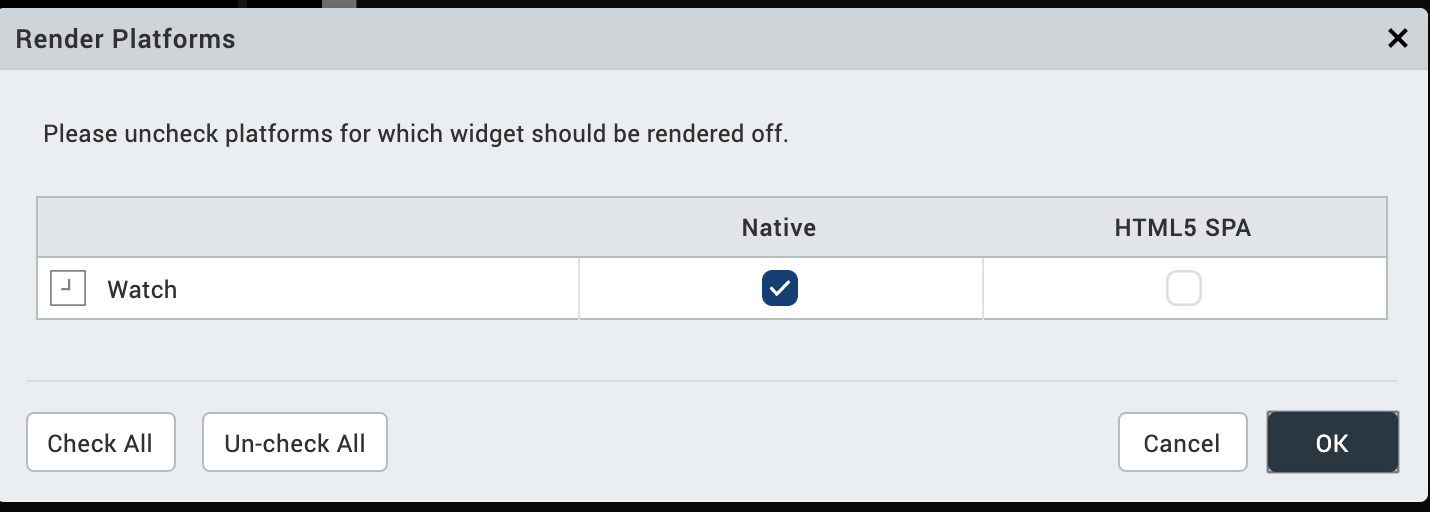
Clear the check box of the platforms for which the widget should not be rendered.
The Difference between Visible and Render
- When a Widget is not rendered for a platform, it implies that the widget is hidden from that specific platform.
- Whereas, when a widget is set as invisible, it implies that the widget is available, but is invisible. This feature is useful when you wanted to display a widget based on certain conditions.
Widget Align
The Widget Align property specifies how the edges of the Button widget are aligned with respect to its parent’s edges. The following alignment options are available:
 | Aligns the left edge of the widget with the left edge of its parent. |
 | Aligns the horizontal center of the widget with the horizontal center of its parent. |
 | Aligns the right edge of the widget with the right edge of its parent. |
 | Aligns the top edge of the widget with the top edge of its parent. |
 | Aligns the vertical center of the widget with the vertical center of its parent. |
 | Aligns the bottom edge of the widget with the bottom edge of its parent. |
Text
Specifies the text that the user sees when running the app.
Width
The Width property sets the x-axis dimension of the widget using the numeric quantity and type of unit that you specify.
You can use the following units of measure to set the width of the widget.
% Specifies the width as a percentage of the parent’s dimensions.
Dp Specifies the width in terms of device independent pixels.
Preferred Size Specifies an optimal width for the widget given the size of the font and the amount of text that the widget displays. The Preferred Size can vary from one platform to another.
Height
The Width property sets the y-axis dimension of the widget using the numeric quantity and type of unit that you specify.
You can use the following units of measure to set the height of the widget.
%. Specifies the height as a percentage of the parent’s dimensions.
Dp. Specifies the height in terms of device independent pixels.
Preferred Size. Specifies an optimal height for the widget given the size of the font and the amount of text that the widget displays. The Preferred Size can vary from one platform to another.
Skin Tab
A widget’s appearance is defined by the skin that is applied to it. Every widget has a skin, even if it’s just the Volt MX Iris default skin. Skins give you the ability to establish visual continuity in your app. On the Skin tab, you can select to use a specific skin for your widget. In addition, you can configure the widget’s background and font.
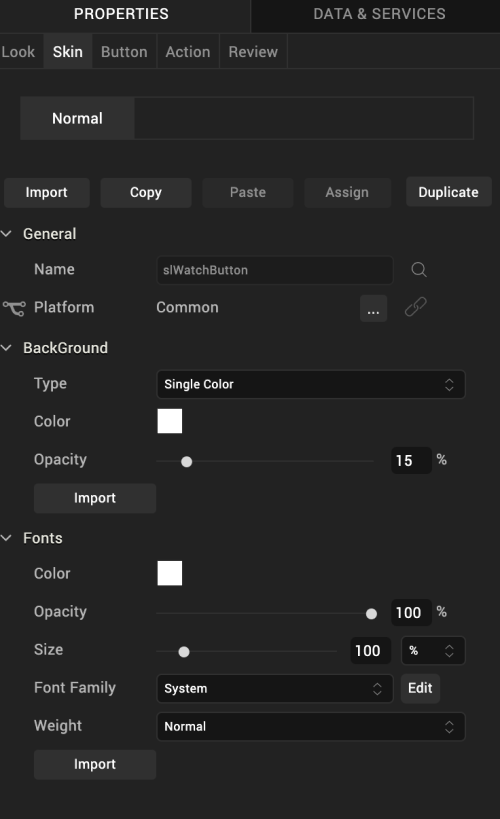
In the Mobile, Tablet, and Desktop channels, a widget may have a number of states, such as Normal (when it’s not being interacted with), Focus (e.g. when it’s been tabbed to), or Pressed. However, the Watch channel has only one button state: Normal.
General
Under the General section of the Skin tab, you can change the name of the skin currently applied (if it’s not one of the default skins), or you can select from the other available button skins by clicking the magnifying glass icon next to the Name text box.
Platform
In channels that support multiple platforms, it’s possible to fork a skin by clicking the Platform ellipsis button  , and then selecting the platforms that you want to fork the widget to. In the case of the Watch channel, currently the only platform available is Watch (Native). For more information, see Forking.
, and then selecting the platforms that you want to fork the widget to. In the case of the Watch channel, currently the only platform available is Watch (Native). For more information, see Forking.
Background
Under the Background section of the Skin tab, you can set the type of background you want to use, and set the color and its opacity.
Type
For the Watch channel, the Button widget is capable of two types of backgrounds:
| Background Type | Description |
| Single Color | Applies a uniform, single color as the background of the skin that you choose. |
| Image | Applies an image of your choosing as the background of the skin. The image stretches to fill the dimensions of whatever widget the skin is applied to. |
Color
If you select Single Color as the background type, you can configure the hue you want by clicking the square color icon and dragging the cursor to the color of your choosing.
Opacity
Similarly, with Single Color as the background type, you can configure the opacity of the background color. By default, the opacity is set to 100, making the background completely opaque with no transparency. However, if you want the background to have a degree of transparency, you can decrease its opacity. To do so, type a value between 0 and 100 in the Opacity text box, or drag the opacity slider to the degree of opacity that you want.
Fonts
Under the Fonts section of the Skin tab, you can set the following properties.
| Property | Description |
| Color | Sets the color that you want the font to be. You configure the hue you want by clicking the square color icon and dragging the cursor to the color of your choosing |
| Opacity | Sets the degree to which the background color is transparent or opaque. By default, the opacity is set to 100, making the background completely opaque with no transparency. However, if you want the background to have a degree of transparency, you can decrease its opacity. To do so, type a value between 0 and 100 in the Opacity text box, or drag the opacity slider to the degree of opacity that you want. |
| Size | You can set the font size by pixels (0 to 600) or as a percentage (0 to 600) of the baseline font size of 28 pixels. |
| Font Family | Currently, the System font is the only font family supported by VoltMX Iris for the Label widget. |
| Weight | You can set the weight of the font either to Normal, which is the default, or Bold. |
For more information, see Understanding Skins and Themes.
Button Tab
On this tab, you configure properties unique to the Button widget. Currently, there is only one.
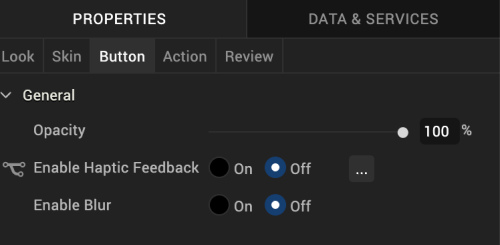
Opacity. Sets the degree to which the widget is transparent or opaque. By default, the opacity is set to 100, making the widget completely opaque with no transparency. However, if you want it to have a degree of transparency, you can decrease its opacity. To do so, type a value between 0 and 100 in the Opacity text box, or drag the opacity slider to the degree of opacity that you want.
Action Tab
On this tab, you define the events that are executed when an action is run. On a Button widget, you can run the following action:
- onClick. This action is invoked by the platform when the user performs a tap action on the button.
For more information on using this action, see Add Actions.
Review Tab
On this tab, you can add and review notes. With the Review Notes feature, you can capture feedback from users who are evaluating your app design. Such requirements capturing helps ensure that the design of your app successfully meets the requirements of potential users. The Review Notes feature supports rich text formatting such as font type and size, paragraph alignment, numbered and bulleted lists, block quotes, and even tables.
For more information, see Capture Product Requirements with Review Notes.