You are here: Appendix B: Android Build Environment and Configurations
Android Build Environment and Configurations
Android developers can customize and configure Android build environments using the following information:
- Access the Generated Android Project for Volt MX Iris Application
- Main Activity and its Life Cycle Methods
- Android Pre-compile and Post-compile Ant Tasks Support
- Support for Integrating Android Third-Party Libraries With Volt MX Iris project
- Network Security Configuration
Access the Generated Android Project for Volt MX Iris Application
If an application is built in Volt MX Iris for the Android platform, a corresponding native Android project is generated.
Changes made to the project can be compiled in the command line using gradle assembleDebug, gradle assembleRelease by navigating to the native Android application folder in the command line.
To access the generated Android project, do the following:
- In Volt MX Iris, in the Project Explorer, on the Project tab, click the context menu arrow for your platform of choice (e.g. Mobile), and then click Open Build Folder.
- Launch Volt MX Iris.
-
In Volt MX Iris, in the Project Explorer, on the Project tab, click the context menu arrow for your platform of choice (e.g. Mobile), and then click Open Build Folder. Open the build folder. A folder opens with the directory structure
<WorkSpace>\temp\<AppID>.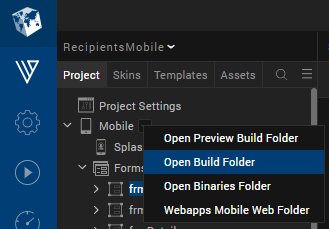
-
Navigate to the respective folder:
- Mobile:
<WorkSpace>\temp\<AppID>\build\luaandroid\dist\<AppID>. - Tablet:
<WorkSpace>\temp\<AppID>\build\luatabrcandroid\dist\<AppID>.
- Mobile:
Main Activity and its Life Cycle Methods
If the application package name is com.xyz.sample and the Application ID is SampleApplication, the Volt MX Iris build process generates a Main Activity Java source file with Application ID as its name in the following path:
- Mobile:
<WorkSpace>\temp\SampleApplication\build\luaandroid\dist\SampleApplication\src\com\xyz\sample\SampleApplication.java - Tablet:
<WorkSpace>\temp\SampleApplication\build\luatabrcandroid\dist\SampleApplication\src\com\xyz\sample\SampleApplication.java
A developer can add custom code and add/modify overridden Android activity life cycle methods such as onCreate(), onStart(), onResume(), onPause(), onStop(), onRestart(), onDestroy(), onNewIntent(Intent), and so on. A developer can also invoke any third-party APIs directly from overridden life cycle methods of the class.
While enhancing the Java file, a developer needs to remember the following points:
- You can enhance the auto-generated methods in this class, but you must not remove any auto-generated code.
- While overriding life cycle methods, you must call the superclass implementation of each life cycle method.
- While using the pre-compile task feature(described in next section), to overwrite the generated Main Activity file with the modified file, a developer may need to maintain separate Main Activity Java source files for debug and release modes, because they differ in certain functions or parameters.
Android Pre-compile and Post-compile Ant Tasks Support
A developer can perform custom tasks before and after compiling the generated native Android application using androidprecompiletask.xml and androidpostcompiletask.xml.
For example, a developer can perform the following pre-compile tasks using androidprecompiletask.xml:
- Overwrite the generated Main Activity Java file with modified file in
<AppID>\src\<packagepath>\folder . - Copy the modified Android application build XML file to the native Android folder.
- Copy any custom libs, assets, res, and other files/folders into the native Android hierarchy.
- Append custom properties to project.properties or local.properties, etc.
For example, you can perform the following post-compile tasks using androidpostcompiletask.xml:
- Automating signing of an application with a release key.
- Trigger a security scan on a generated APK for security flaws.
- Trigger automation on a compiled APK file and publish results.
- Check-in code in GIT repositories.
A developer can copy these XMLs into Volt MX Iris project workspace base directory with same names (androidprecompiletask.xml and androidpostcompiletask.xml).
A template androidprecompiletask.xml file is available at <WorkSpace>\temp\<AppID>\build\luaandroid\extres. This XML is available under extres folder after building any sample project. This XML file contains build parameter information useful to perform the tasks explained in the example above.
Note: The pre- and post- compile Ant tasks can support integration with external tools such as binary protection tools, static analyzer tools, and so on.
Support for Integrating Android Third-Party Libraries With Volt MX Iris project
Since VoltMX's build system is based on Gradle, integrate third party Android library format (.aar) files into the project by copying .aar files to the required path.
Similarly, third-party java class (.jar) files can also be integrated into the project by copying .jar files to the required path.
Introduction
From HCL Volt MX 9.x onwards, FFIs need to be converted into NFIs. For the Android Channel we can convert them by following the steps below. These steps are applicable only to the Android Channel. For iOS, customers can create a case with HCL Support to have them converted.
Instructions
-
Take any sample NFI zip file you have. In this example we have used the VoltMX_FileStorage-Android-4.0 NFI file which comes pre-configured with the VoltMX client. This NFI file can be found under Project Name --> nativebindings --> Android --> 4.0.
-
Create a new folder outside of the Workspace folder, for example NFI ZipFiles. Copy the sample NFI zip file (VoltMX_FileStorage-Android-4.0) into the folder.
-
Rename the NFI zip file to your FFI name .zip extension. In this example, we renamed VoltMX_FileStorage-Android-4.0 to Voltmx_MYFFINAME-Android-4.0.zip which matched the name of our FFI file.
-
Unzip the zip file that was renamed in step 3, and rename the directory in the file to match the name created in step 3. In this example, we renamed it to Voltmx_MYFFINAME-Android-4.0.
-
In the zip file opened in Step 4, open the metadata.properties file and you should see the following default values:
moduleName=VoltMX_FileStorage
moduleVersion=1.0
moduleDescription=VoltMX_FileStorage
os=Android
sdkVersion=4.0
Update the moduleName and moduleDescription based on the name you have provided in step 3. In this example we updated them to Voltmx_MYFFINAME:
moduleName=Voltmx_MYFFINAME
moduleVersion=1.0
moduleDescription=Voltmx_MYFFINAME
os=Android
sdkVersion=4.0
-
Navigate to the thirdparty directory of the opened zip file and delete the jar located inside.
-
Copy your original FFI aar or jar file and paste it into the folder where the jar file was just deleted
-
Zip the folder renamed in Step 4 ,This will generate a zip file for a SINGLE FFI. You need to follow the same approach for all FFIs you need to generate.
-
Once you are done with manually creating the zip file, you need to import it into Iris/Visualizer:
a) From Iris select Edit --> Manage Native Function API(s) --> Android.
b) Click on Import and select the zip file generated in the steps above.
Note : When you are importing as an NFI, you need to delete the JARS/AARs for which you have generated as an NFI, and the respective code calls should also be deleted in your application logic.
If the library format's .aar or .jar file depends on other libraries, add them to your project.
Important: If the included dependencies have an associated order among them, they must be added in same order. For more information on dependency order, see Dependency order.
For Volt MX Iris, use the build.gradle entries to Suffix Gradle property to add dependencies. For example, if your .aar file or .jar file depends on Appcompat and Play Services Analytics, you can add the following dependency entries.
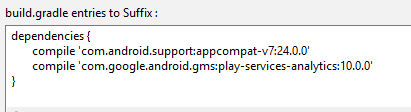
For information on Gradle properties, see Set Native App Properties.
< concat destfile = "${app.dir}/build.gradle"
append = "true" > $ {
line.separator
}
dependencies.compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:24.0.0' < /concat>
< concat destfile = "${app.dir}/build.gradle"
append = "true" > $ {
line.separator
}
dependencies.compile 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-analytics:10.0.0' < /concat>
Network Security Configuration
For privacy policy Google Android has changed the network security configuration from Android 9 (API level 28 ) and upper versions.
Starting with Android 9 (API level 28), cleartext support is disabled by default. previous it is by default enabled ( upto Android 8.1(API level 27)) .
So if you want build starting with Android 9 ( API level 28) you have to allow android:usesCleartextTraffic="true" .
Two ways you can allow: * You can write code level inside your app - res/xml/network_security_config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <network-security-config> <domain-config cleartextTrafficPermitted="true"> <domain includeSubdomains="true">api.example.com(to be adjusted)</domain> </domain-config> </network-security-config>
- You can use as a TAG in Iris setting