Flex Pseudocode Examples
Volt MX Application Design and Development Guidelines: Flex Layout Guidelines > Flex Pseudocode Examples
Flex Container Pseudocode Examples
Below are some of the Pseudocode examples and their images:
Building a grid of widgets
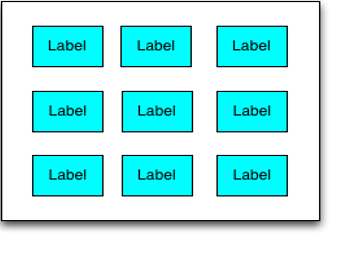
//Sample code to build a grid of widgets.
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
c.setDefaultUnit(dp);
c.width = 170;
c.height = 170;
wWidth = 30;
wHeight = 20;
wSpacing = 20;
for (int I = 0; I < 3; I++ )
{
for (int J = 0; J < 3 ; J++)
{
var label = new Label(“id”, “Label”)
label.width = wWidth;
label.height = wHeight;
label.top = (I + 1)* spacing + I* wHeight;
label.left = (J + 1)* spacing + J * wWidth;
c.add(label);
}
}
Position the widgets diagonally
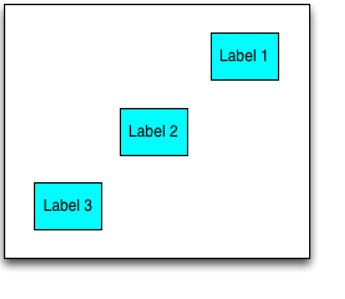
//Sample code to position the widgets diagonally.
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
c.setDefaultUnit(dp);
var label1 = new Label(“id”,“Label1”)
c.add(label1);
var label2 = new Label(“id”,“Label2”)
c.add(label2);
var label3 = new Label(“id”, “Label3”)
c.add(label3);
c.doLayout = function()
{
wWidth = 30;
wHeight = 20;
wSpacing = 20;
label1.width = label2.width = label3.width = wWidth;
label1.height = label2.height = label3.height = wHeight;
label1.right = 20
label1.top = 20;
label2.left = c.frame.width/2 - wWidth/2
label2.top = c.frame.height/2 - wHeight/2
label3.left = 20;
label3.bottom = 20;
}
Position the widgets relative to siblings
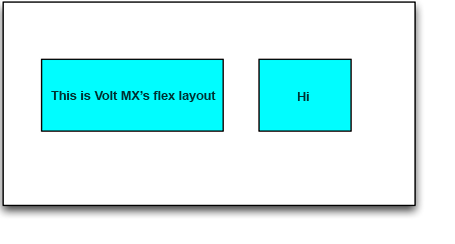
//Sample code to position the widgets relative to siblings
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
var label1 = new Label(“Hi”)
c.add(label1);
var label2 = new Label(“Hi”)
c.add(label2);
label1.left = 20;
label1.top = 30
label1.width = voltmx.flex.USE_PREFERRED_SIZE
label1.height = 40
label1.doLayout = function(){
var lab = this.parent.label2; // accessing the child’s through parent
lab.left = 20 + label1.frame.width /2;
lab.left.top = 30;
label2.width = label1.frame.width /2
label2. height = 40
}
Overlapping the widgets using zIndex
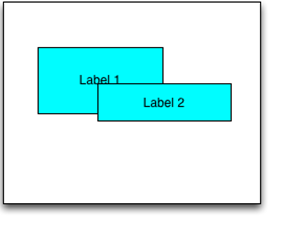
//Sample code to overlap the widgets using zIndex
var label1 = new Label("id", "Label1")
label1.zIndex = 1;
c.add(label1);
var label2 = new Label("id", "Label2")
label1.zIndex = 2;
c.add(label2);
label1.left = 20;
label1.top = 30
label1.width = 60
label1. height = 50
label1.doLayout = function(){
label2.left = 20 + label1.frame.width /2;
label2.top = 30 + label1.frame.height/2
label2.width = 80
label2. height = 25
}
Positioning the widgets horizontally
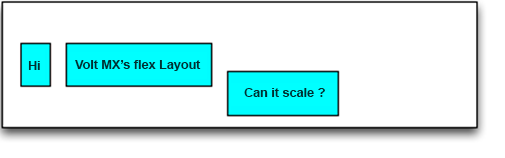
//Sample code to position the widgets horizontally
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
//set the container layout type as VoltMX.Flex.FLOW_HORIZONTAL;
var label1 = new Label("id", "Hi")
c.add(label1);
var label2 = new Label("id", "VoltMX’s Flex Layout")
c.add(label2);
var label3 = new Label("id", "Can it scale ?")
c.add(label3);
label1.top = label2.top = 20;
label3.top = 30
label1.left = label2.left = label3.left = 5;
label1.width = label2.width = label3.width = voltmx.flex.USE_PREFERRED_SIZE
label1.height = label2.height = label3.height = 50
Stacking the widgets vertically
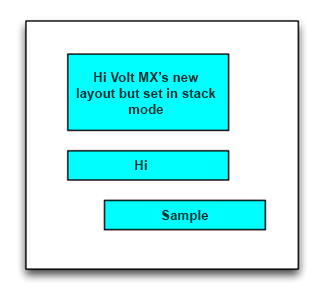
//Sample code to stack the widgets vertically
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
//set the container layout type as VoltMX.Flex.FLOW_VERTICAL;
var label1 = new Label(“id”, “Hi VoltMX’s new layout but set in stack mode”)
c.add(label1);
var label2 = new Label(“id”, “Hi”)
c.add(label2);
var label3 = new Label(“id”, “Sample”)
c.add(label2);
label1.left = label2.left = 30;
label3.left = 40
label1.top = label2.top = label3.top = 5;
label1.width = label2.width = label3.width = 60
label1.height = label2.height = label3.height = voltmx.flex.USE_PREFERRED_SIZE
Wrapping the text when it reaches the specified width
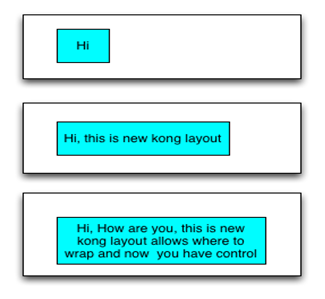
//Sample code to wrap the text when it reaches the specified width
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
var label1 = new Label("id", "text")
c.add(label1);
label1.text = // Data is fed from net work
label1.left = 20;
label1.top = 20;
label1.maxWidth = 80
label1.height = voltmx.flex.USE_PREFERRED_SIZE
Wrapping the text when it reaches the parent boundaries

//Sample code to wrap the text when it reaches the parent boundaries
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
var label1 = new Label(“id”, “text”)
c.add(label1);
label1.text = // Data is fed from net work
c.doLayout = function()
{
label1.left = 20;
label1.top = 20;
label1.maxWidth = c.frame.width - 20
label1.height = voltmx.fLex.USE_PREFERRED_SIZE;
}
Widget occupying the available horizontal space

//Sample code of widget occupying the available horizontal space
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
var label1 = new Label("id", "text")
c.add(label1);
label1.text = // Data is fed from net work
label1.left = 20;
label1.top = 20;
label1.right = 0;
label1.height = voltmx.flex.USE_PREFERRED_SIZE
Widget occupying the available vertical space
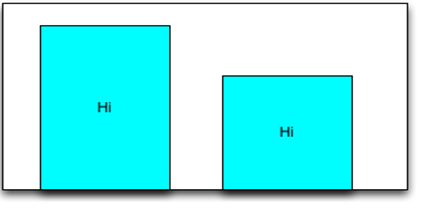
//Sample code of widget occupying the available vertical space
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
var label1 = new Label("id", "Hi")
c.add(label1);
var label2 = new Label("id", "Hi")
c.add(label2);
label1.left = 20;
label1.top = 20;
label2.right = 30;
label2.top = 50;
label1.bottom = 0;
label1.width = 50;
widget to occupy its preferred size without any given height or width

//Sample code of a widget to occupy its preferred size without any given height or width
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
c.clipBounds = false;
var label1 = new Label(“id”, “text”)
c.add(label1);
label1.text = // Data is fed from net work
label1.left = 20;
label1.top = 20;
Widget position in center and offset from left and right boundaries
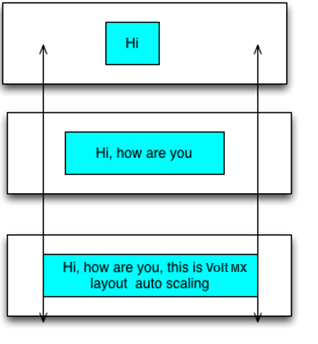
//Sample code of widget position in center with width to grow maximum and with a minimum
offset from left and right boundaries.
var c = new voltmx.ui.FlexContainer();
var label1 = new Label("id", "text")
c.add(label1);
label1.text = // Data is fed from net work
label1.minWidth = 20;
label1.maxWidth = 80;
label1.height = voltmx.flex.USE_PREFERRED_SIZE
label1.center = {80,80};