JSON Adapter
User Guide: Integration > Configure the Integration Service > JSON Adapter
JSON Adapter
A service that communicates with an external data source using JSON over the HTTP protocol, and returns a response in JSON format is known as a JSON Service. You can use the JSON services in any case where you would use an XML service. But, the response of a JSON service is in a JSON format.
Concepts about JSON Adapter
Notations
- JSON Object - {}
- JSON Array - []
Important Considerations
- JSON Array will consist of an array of JSON Objects or a blank array.
- JSON Object is a key value pair. The key is a String and value can be a String, number(int, float,double), JSON Object or JSON Array.
- JSON string will not contain attributes.
- JSON path does not provide Axes like Xpath.
- For JSON Path, if a JSON backend contains a collection, the parameters set should be same for all the records in the collection. For example, if the collection has parameters:
nameandtype, these parameters should be repeated in the backend response, shown in the following sample code:
// Sample code from a response:
{"GlossDef":{"para":"A meta-markup language, used to create markup languages such as DocBook.","GlossSeeAlso":[{"name":"test","type":"XML"},{"name":"tester","type":"HTML"}]}}
-
For XPath, if a JSON backend contains a collection, the fetch
only a parameter from the record, the XPath should be in<record>/<collection>[*]/<parameter>, which includes an[*].For example, in the previous sample code, if you want to fetch
namefrom theGlossSeeAlso, the sample XPath should be as follows:
// Sample code to fetch only the **name** parameter from a record, XPath:
/GlossDef/GlossSeeAlso[*]/name
Selecting Elements
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| elementname | Selects all child elements of the named Element. |
| // | Selects elements in the document from the current element that match the selection no matter where they are. |
Example
| Path Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| bookstore (or) /bookstore | Selects all the child elements of the bookstore element |
| bookstore/book | Selects all book elements that are children of bookstore |
| //book | Selects all book elements no matter where they are in the JSON string |
| bookstore//book | Selects all book elements that are descendant of the bookstore element, no matter where they are under the bookstore element |
Predicates
Predicates are used to find a specific element or an element that contains a specific value. Predicates are always embedded in square brackets.
| Path Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| bookstore/book[0] | Selects the first book element that is the child of the bookstore element |
| bookstore/book[last()] | Selects the last book element that is the child of the bookstore element |
| bookstore/book[last()-1] | Selects the last but one book element that is the child of the bookstore element |
| bookstore/book[position()<3] | Selects the first two book elements that are children of the bookstore element |
| bookstore/book[price>35.00] | Selects all the book elements of the bookstore element that have a price element with a value greater than 35.00 |
| bookstore/book[price>35.00]/title | Selects all the title elements of the book elements of the bookstore element that have a price element with a value greater than 35.00 |
Note: If a key name contains a value with a dot (
.), the path for the same should be in double quotes ([""]). For example, if the key in response is<element1>.<element2>, the path must be as["<element1>.<element2>"]
Operators
| Operator | Description | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| > | Greater than | price>9.80 | true if price is 9.90 false if price is 9.80 |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | price>=9.80 | true if price is 9.90 false if price is 9.70 |
| < | Less than | price<9.80 | true if price is 9.00 false if price is 9.80 |
| != | Not equal | price!=9.80 | true if price is 9.90 false if price is 9.80 |
| \= | Equal | price=9.80 | true if price is 9.80 false if price is 9.90 |
Configure JSON End-point Adapter
To configure a JSON service in Integration service definition tab, follow these steps:
- In the Name field, provide a unique name for your service.
-
From the Service Type list, select JSON.
Note: XML is selected, by default.
-
Provide the following details to create a JSON service.
Fields Description Path Expression You can choose between JSON Path or XPath expressions to process and transform the data from the backend response.> Note: JSON Path is the recommended option for a JSON service. (Requires Volt MX Foundry runtime version 8 with Service Pack 3 or higher)> Note: To walk-through creating automated response parameters for a JSON service by using the Tree view with Volt MX Foundry, take a look at our hands-on tutorial for UI to view and create a Service Response. Version Specify the version number for the service. Base URL Type the URL. Identity Service for Backend Token Select the Identity service associated with your app if this service needs backend token like access_token from that Identity service to access the backend server.
Select one of the following modes:
**None**: Select this option if you do not want to provide any authentication for the service.**Basic**: Provide User ID and Password if the external Web service requires a form or basic authentication.**NTLM**: Your service follows the NT LAN Manager authentication process. You are required to provide the User ID, Password, NTLM Host, and NTLM Domain.
-
For additional configuration of your service definition, provide the following details in the Advanced section.
Field Description Specify JAR To specify a JAR associated to the service, select one from the Select Existing JAR drop-down menu or click Upload New to add a new JAR file. Make sure that you upload a custom JAR file that is built on the same JDK version used for installing Volt MX Foundry Integration.You can download the uploaded jars to your local system. API Throttling If you want to use API throttling in Volt MX Foundry Console, to limit the number of request calls within a minute. do the following: In the Total Rate Limit text box, enter a required value. This will limit the total number of requests processed by this API.In the Rate Limit Per IP field, enter a required value. With this value, you can limit the number of IP address requests configured in your Volt MX Foundry console in terms of Per IP Rate Limit. To override throttling from Volt MX Foundry App Services Console, refer to Override API Throttling Configuration. URL Provider Class Enter the qualified name of the URL Provider Class. For more information, refer URL Provider Support for XML, JSON, SOAP, and API Proxy. Note: All options in the Advanced section are optional.
-
Enter the Description for the service.
- Click SAVE to save your service definition.
Create Operations for JSON
The Operation List tab appears when you click Add Operation in the Service Definition page.
Note: Click Operations List tab > Configure Operation. The Configured Operations list appears.
-
To create an operation, follow these steps:
-
Click SAVE & ADD OPERATION in your service definition page to save your service definition and display the NewOperation tab for adding operations.
OR
Click Add Operation to add a new operation or from the tree in the left pane, click Add > Add New Operation.
Click to View image
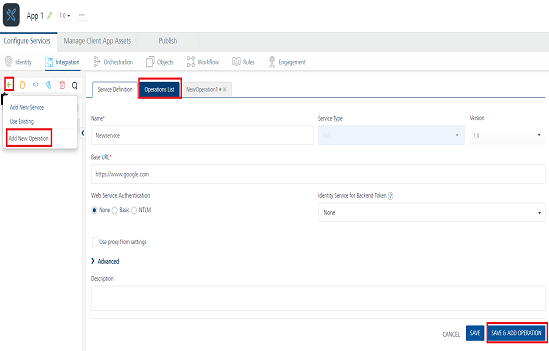
Note: To use an existing integration service, refer to How to Use an Existing Integration Service.
- Click Add Operation. The selected operations appears under Configured Operations list.
- Provide the following details to create an operation.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The operation name appears in the Name field. You can modify the name, if required. |
| Operation Security Level | It specifies how a client must authenticate to invoke this operation. |
| Authenticated App User – It restricts the access to clients who have successfully authenticated using an Identity Service associated with the app.Anonymous App User – It allows the access from trusted clients that have the required App Key and App Secret. Authentication through an Identity Service is not required.Public – It allows any client to invoke this operation without any authentication. This setting does not provide any security to invoke this operation and you should avoid this authentication type if possible.Private - It blocks the access to this operation from any external client. It allows invocation either from an Orchestration/Object Service, or from the custom code in the same run-time environment. Note: The field is set to Authenticated App User, by default. | |
| Target URL | The Target URL field is pre-populated with the URL. You can add the suffix, if required.http://baseurl.com/suffixFor Example, to the base URL, you can add suffix such as /latest or /sports to get latest news or sports news:`http://feeds.foxnews.com/foxnews/latest |
`http://feeds.foxnews.com/foxnews`/sports` |
response operations, provide the following details in the Advanced section.
Custom Code Invocation You can add pre and post processing logic to services to modify the request inputs. When you test, the services details of various stages in the service execution are presented to you for better debugging. All options in the Advanced section are optional. For more details, refer to Preprocessor and Postprocessor. Additional Configuration Properties Additional Configuration Properties allows you to configure service call time out cache response. For information on different types of configuration properties, refer Properties. Pass-through Cookies Pass-through Cookies allows you send cookies present in the incoming client request to the backend target request. For detailed information, refer Pass-through Cookies. Front-end API Front-end API allows you map your endpoint ](or) backend URL of an operation to a front-end URL. For detailed information, refer Custom Front-end URL. Stub Backend Response Stub Backend Response allows you enable a stub back-end service. To enable Stub Backend Response, refer How to Enable Stub Back-end Response.For more details on Stub back-end response, refer to How to Develop Apps based on a Stubbed Service. Server Events Using Server Events you can configure this service to trigger or process server side events. For detailed information, refer Server Events.
Note: All options in the Advanced section for operations are optional.
- Enter the Description for the operation.
Configure Request Operation for JSON
Integration services accept only form-url-encoded inputs for all input parameters provided in service input parameters (request input).
You can perform the following actions in Request Input tab:
- Click Add Parameter to add an entry (if the entries for input and the output tabs does not exist).
- To make duplicate entries, select the check box for the entry, click Copy and Paste.
- To delete an entry, select the check box for an entry and click Delete .
-
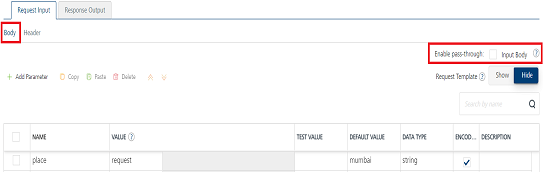
Under the Body tab, perform the following actions:
-
To forward the body of the client's request to backend as it is, select the Enable pass-through input body check box. For more details on API Proxy service, refer to How to Enable Pass-through Proxy for Operations.
-
To configure parameters in the clients body, do the following:
-
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter the name for the request input parameter. |
| Value | Three different options are available in Volt MX Foundry under VALUE during configuration of any operation. When you start editing this field, dependent identity services are auto populated. These options primarily determine the source of the value of the header. Request: If this option is selected, the Integration Server picks the value pairs from the client's request during run time and forwards the same to the back-end.User has the option to configure the default value. This default value is taken if the request does not have the header.Session: If this option is selected, the value of header is picked from session context based on the user configuration.Identity: If this option is selected, you can filter the request parameters based on the response from the identity provider. For more details to configure identity filters, refer to Enhanced Identity Filters - Integration Services. Note: The field is set to Request, by default. |
| TEST VALUE | Enter a value. A test value is used for testing the service. |
| DEFAULT VALUE | Enter the value, if required. The default value will be used if the test value is empty. |
| Scope | Select request or session. This field is set to Request, by default. |
| Encode | Select the checkbox to enable an input parameter to be encoded. For example, the name New York Times would be encoded as New_York_Times when the encoding is set to True. The encoding must also adhere the HTML URL encoding standards. |
-
Click the Header tab to provide the following custom headers for an operation.
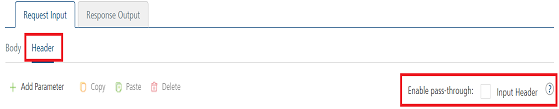
You must provide the custom HTTP headers based on the operation. For example, post or get.
Perform the following actions to provide the custom header:
- To forward headers of the client's request to backend as it is, select the Enable pass-through input header check box. For more details on API Proxy service, refer to How to Enable Pass-through Proxy for Operations.
- To configure parameters in the client's header, do the following:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Provide custom HTTP headers required by the external source. |
| Value | Three different options are available in Volt MX Foundry under VALUE during configuration of any operation. When you start editing this field, dependent identity services are auto populated. These options primarily determine the source of the value of the header. Request: If this option is selected, the Integration Server picks the value pairs from the client's request during run time and forwards the same to the back-end.User has the option to configure the default value. This default value is taken if the request does not have the header.Session: If this option is selected, the value of header is picked from session context based on the user configuration.Identity: If this is selected, you can filter the request parameters based on the response from the identity provider. For more details to configure identity filters, refer to Enhanced Identity Filters - Integration Services. Note: The field is set to Request, by default.> Note: If the header value is scoped as a Request (or) Session and the same header is accessed under the Expression header value, then the expression must be represented as $request.header (or) $session.header.Example: If a header 1 value is a request and header 2 value is an expression, then the value of the expression must be $Request.header1.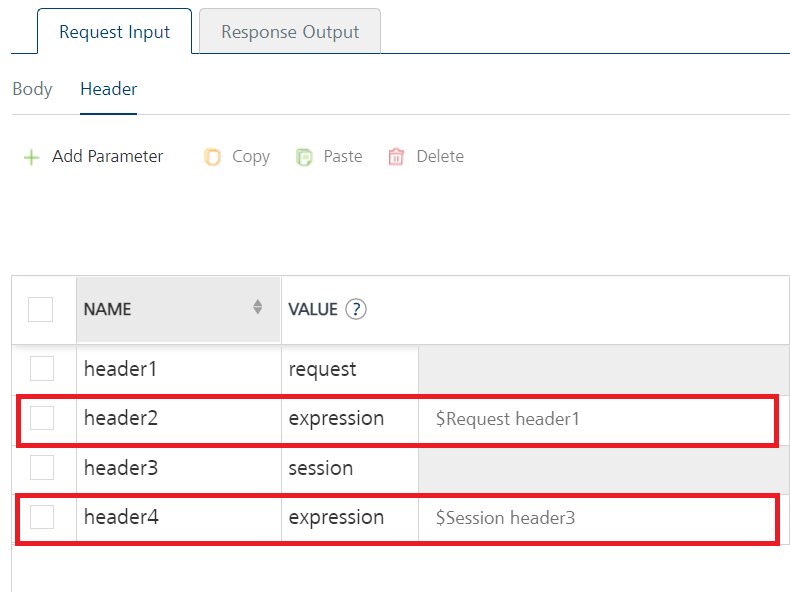 Note: If the header value is scoped as a Request, and the bearer token is passed when the operation security level is Public, the X-Voltmx-authorization code should also be passed as Request. Note: If the header value is scoped as a Request, and the bearer token is passed when the operation security level is Public, the X-Voltmx-authorization code should also be passed as Request.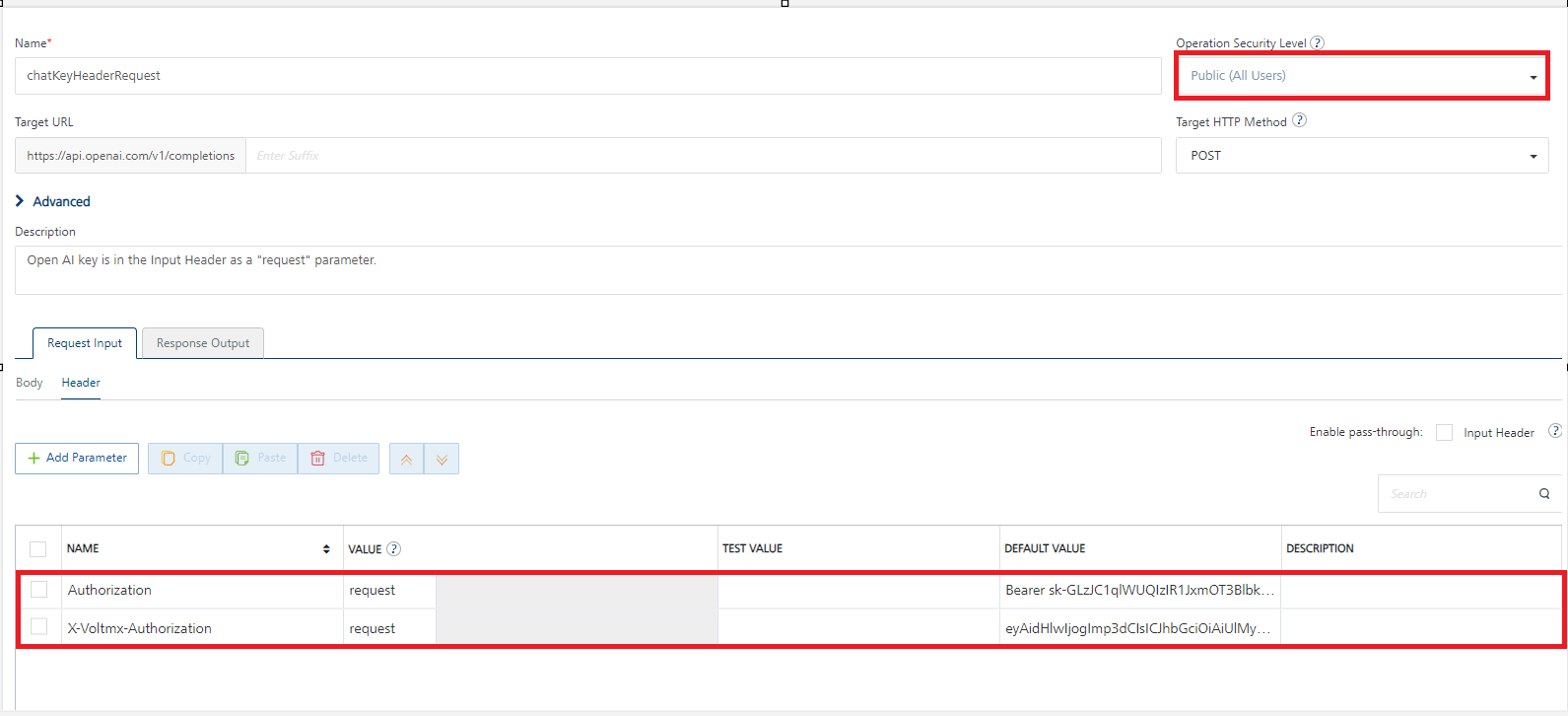 |
| TEST VALUE | Enter a value. A test value is used for testing the service. |
| DEFAULT VALUE | Change the syntax, if required. The default value will be used if the test value is empty. |
| Description | Enter a proper description. |
- You can add pre and post processing logic to services to modify the request inputs. When you test, the services details of various stages are displayed in the service execution for better debugging. You can refer to Test a Service Operation for the steps to test a service.
Configure Response Operation for JSON
Click Response Output tab to configure the fields of the table for displaying the data.
Note: If you define parameters inside a record as the session, the session scope will not get reflected for the parameters.
- To forward the response from the backend to the client as it is, select the Enable pass-through output body check box. For more details on API Proxy service, refer to How to Enable Pass-through Proxy for Operations.
-
You can configure XPath or JSON path expressions for extracting the required elements from the back-end response of the service call. So that the extracted output can be sent to the client app. Based on the path expression selected in the service definition, you can create an XPath or JSON path manually. For JSON services only, JSON Path can be auto-generated.
Note: Auto generation of XPath support is available from Volt MX Foundry V8 SP3 onwards.
The following table details XPath/JSON generation:
To create JSON Path automatically(for V8 SP4) in case if you have selected JSON Path in the Path Expression field, follow these steps To create XPath/JSON Path manually After you click Save and Fetch Response, the Tree view with the back-end response appears by default in the Test > Backend Response pane. Click or hover your mouse cursor over the node for which you want to create JSON Path. The Create response button appears next to that node. Click the Create response button. 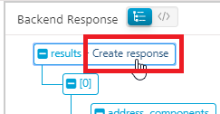 A new row is created automatically along with the JSON Path for the selected node in the Response Output tab. > Note: The Response Output tab appears if you have clicked the Create response button from the Request Input tab.
A new row is created automatically along with the JSON Path for the selected node in the Response Output tab. > Note: The Response Output tab appears if you have clicked the Create response button from the Request Input tab.> Important: If you have selected the Path Expression as JSON Path, in the Response Output tab, the Add All to Response Output cogwheel is displayed. You can generate JSON Path for the entire response by clicking the Add All to Response Output button.
 |
| Click Add Parameter to add new row. Click the Tree button in the Backend Response tab. This displays the backend response in a tree structure format. Click the node for which you want to create XPath/JSON Path. The XPath/JSON Path for that node is displayed at the bottom of the Tree structure.
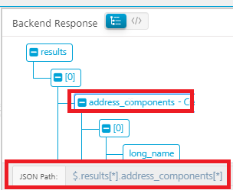 Enter that XPath/JSON Path in the row that you have created.
Enter that XPath/JSON Path in the row that you have created.| | | |
-
To configure parameters in the response, enter the values for required fields such as name, path, scope, data type, collection ID, record ID, format and format value.
Enter the values for required fields such as name, path, scope, data type, collection ID, record ID, format and format value.
ID Path city //current_observation/display_location/city latitude //current_observation/display_location/latitude longitude //current_observation/display_location/longitude temperature //current_observation/temp_c relative_humidity //current_observation/relative_humidity windspeed //current_observation/wind_string icon //current_observation/icon icon_url //current_observation/icon_url forecast_url //current_observation/forecast_url Important: If the back-end for an XML service provides the date in a specific format and you want send the date in a different format to a device, you can configure the data format and FormatValue ( syntax :
inputDateFormat~outputDateFormat) in the response tab.For example, if a back-end sends the date as
Thu, 07 Sep 2017 07:03:00 GMTand you want convert it to2017-09-07T07:03:00.000+0000, then set the format value asEEE, dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss z~yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ.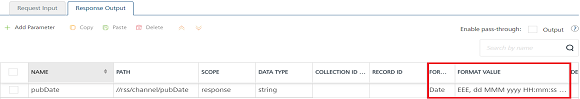
For more details on the syntax of the date formats, refer https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/text/SimpleDateFormat.html
Note: When you enable Pass-through proxy flags, you will notice that you cannot configure request input, headers, and response out parameters for this operation.
-
To validate the operation details, click Save and Test. For more details, refer to Test a Service Operation.
-
Click Save Operation to save the changes.
To use an existing integration service, refer to How to Use an Existing Integration Service.
Note: You can view the service in the Data Panel feature of Volt MX Iris. By using the Data Panel, you can link back-end data services to your application UI elements seamlessly with low-code to no code. For more information on Data Panel, click here.